What is liposomal iron?
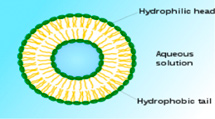
Liposomal Iron, is a new technology based on ferric pyrophosphate carried within a phospholipid membrane of plant origin (soya), which compared to other formulations based on iron, has high gastrointestinal absorption, high bioavailability and lower incidence of side effects.
ABSORPTION AND BIOAVAILABILITY
The Liposomal Iron, is a preparation based on ferric pyrophosphate carried within a phospholipid membrane of plant origin (soya), which compared to other formulations based on iron, it has high gastrointestinal absorption and high bioavailability, and
lower incidence of side effects
Iron daily supplementation and women
Absorption of ionic iron occurs mainly at the duodenal level and is mediated by specific carriers. Under normal conditions, only 15-20% of the administered iron is absorbed, so it does not make sense to force the transport capacity of the carriers with high doses. The sophisticated incorporation technology in natural phospholipids makes the iron highly bioavailable, well tolerated and rapidly absorbed. The presence of the liposomal envelope, in fact, protecting the iron from contact with the gastric mucosa avoids the pro-oxidant effect of free iron. The liposomal protection allows the microelement to overcome the gastric environment unscathed to be absorbed directly at the level of the whole small intestine and not only duodenal. These natural vehicles, in fact, are the dense and voluminous lipoproteins that represent the form of transport of food fats from the intestine to the various tissues. The ingested iron liposome in the intestinal lumen is absorbed directly by the M cells (and not by the enterocytes), cells that originate from the lymphatic system and are located throughout the small intestine. Subsequently, the liposome is incorporated by endocytosis from the macrophages and through the lymphatic stream reaches, intact, the hepatocytes. Within the hepatocytes the liposome will be “opened” by the lysosomal enzymes thus making the iron available for the organism. The absorption and bioavailability of the liposomal iron compared to the other iron salts, commonly used in the formulation of the products present on the market, has been evaluated on an animal model. These studies have shown that thanks to liposomal technology, the absorption of liposomal pyrophosphate iron is 3.5 times greater than free pyrophosphate iron, 2.7 times higher than iron sulphate and 4.1 times higher than the iron gluconate. In addition, the plasma concentration of liposomal iron was found to be maximal after two hours from intake, which ensures greater bioavailability of the element for all metabolic processes.

It is estimated that more than 40% of pregnant women worldwide are anaemic. At least half of this anaemia burden is assumed to be due to iron deficiency.
Pregnant women require additional iron and folic acid to meet their own nutritional needs as well as those of the developing fetus. Deficiencies in iron and folic acid during pregnancy can potentially negatively impact the health of the mother, her pregnancy, as well as the fetal development.
Evidence has shown that the use of iron and folic acid supplements is associated with a reduced risk of iron deficiency and anaemia in pregnant women.
IFA and Pregnancy
Iron deficiency is caused by inadequate iron intake to meet normal requirements or increased requirements due to excessive blood loss and reproduction. Giving iron and folic acid (IFA) supplements to pregnant women to prevent and treat anemia is a policy in most developing countries. All pregnant women need iron because a woman will become iron deficient with or without anemia by the end of her pregnancy, if she does not take iron supplements (Lynch, 2000). Giving iron supplementation to children younger than five years of age is not a policy in all countries, a few countries are continuing the practice of supplementing with iron and have taken it to scale. Premature and low-birth-weight infants need additional iron starting at two months of age.
WHO recommendations for pregnant women
The World Health Organization recommends a daily supplementation of oral iron with 30 mg to 60 mg of elemental iron and 400 µg (0.4 mg) of folic acid for pregnant women to prevent maternal anaemia, puerperal sepsis, low birth weight, and preterm birth.
IronFast main ingredients
Each capsule contains Iron 14mg, Vitamin C 35mg, Vitamin B12 1.3mcg and Folic acid 200mcg.
Pack of 30 caspules
Indications
Supplement of Iron, Vitamin C, Vitamin B12 and Folic acid, which contributes a supplement share of these nutrients in the event of food shortages or increased needs for adult and pregnant women.
A wide range of clinical trials is available upon request

